The Science Of Scientific Writing Set 9 Set 9-Analysis maps • Second page • Example • Exercise 1 • Exercise 2 • Exercise 3 • Exercise 4 • Exercise 5 • Refinement Revisited • Rabbit Rule • Holding Hands Rule • Exercise 6 • Inference objections • Exercise 7 • Exercise 8 • Final.
OVERVIEW: The way to well-written science
PART I: Paragraphs and Sentences
SET A: Paragraphs: The Maps Behind Them
SET B: Paragraphs: Using Maps to Meet Readers' Expectations
SET C: Paragraphs with Something Extra: Points and Tails
SET D: The Generic Section: Expectations and Maps as Blueprints
SET E: Scientific Sections: The Methods and Results
SET F: Scientific Sections: The Discussion
SET G : Scientific Sections: The Introduction
SET H : Sentences
SET I : The Paper as a Whole
PART II: The Paper and its Sections
SET 1: Argument Parts
SET 2: Indicator Words
SET 4: Locating Arguments in Prose
SET 5: Rationale's Essay Planner
SET 6: Evidence in Arguments: Basis Boxes
Synthesis 1: Position-Early Paragraphs
Synthesis 2: Position-Final Paragraphs
Synthesis 3: Writing a Discussion I
Synthesis 4: Writing a Discussion II
Did your map look like this?
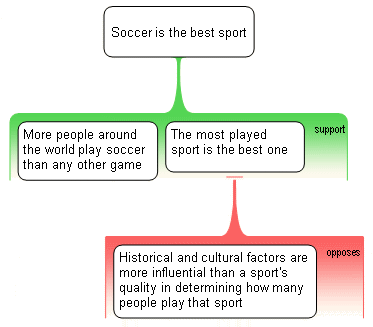
The objection bears on the assumption, so it needs to be connected to that claim box, rather than the whole reason. Don't map it like this:
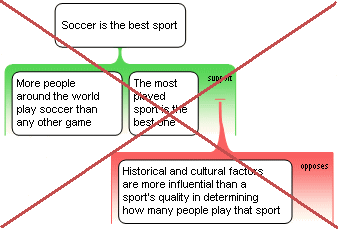
This map suggests there is something wrong with the reason other than a problem with one of the claims we've identified.
Content of this page drawn in whole or part from the Austhink Rationale Exercises with permission from Austhink.